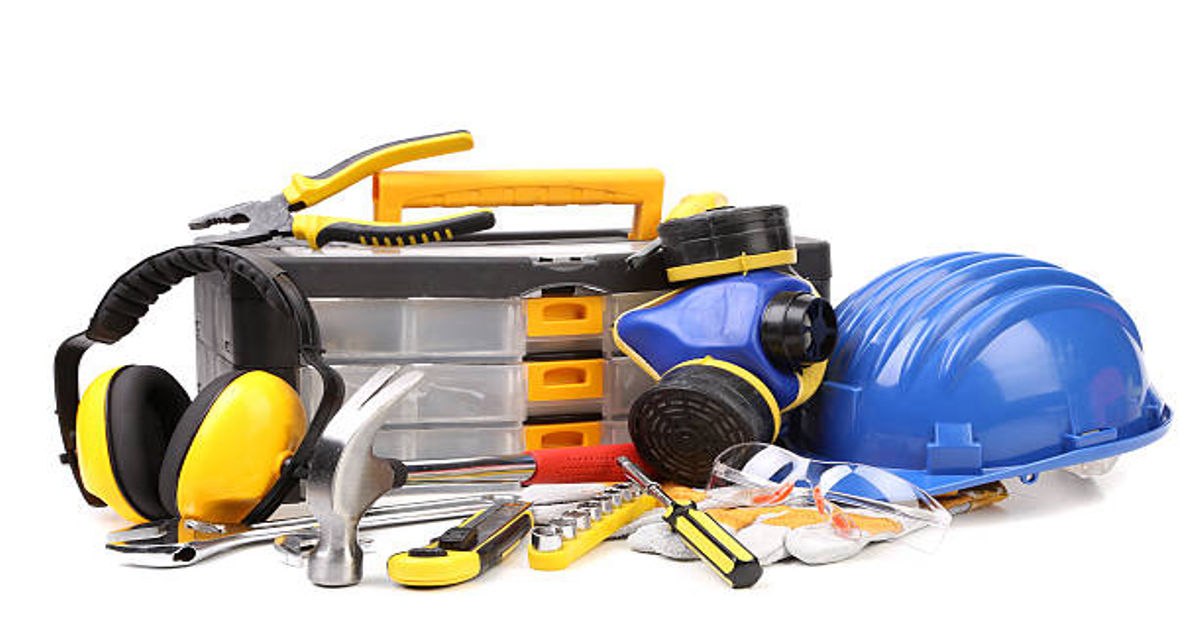
In every industry, from construction and manufacturing to warehousing and logistics, the quality and reliability of supplies determine the overall productivity and safety of operations. PLG supplies—short for Procurement, Logistics, and General supplies—represent a vast category of essential products that support day-to-day industrial activities. These include tools, safety gear, maintenance materials, storage systems, and consumables that form the backbone of operational efficiency.
Whether it’s a construction worker using a safety helmet, a warehouse team handling packaging materials, or maintenance staff managing repair tools, PLG supplies ensure the seamless functioning of every task. This article explores in detail what PLG supplies encompass, their categories, importance, benefits, and how businesses can effectively manage them for maximum efficiency.
1. Understanding PLG Supplies
PLG supplies refer to a wide range of industrial, maintenance, and safety materials procured and used across various sectors. These items are not only essential for operational continuity but also for ensuring workplace safety and compliance with regulations.
The term “PLG” can be broken down into three parts:
| Component | Meaning | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| P (Procurement) | The sourcing and purchasing of essential tools and materials | Supplier relationships, purchasing systems, budgeting |
| L (Logistics) | The storage, handling, and transportation of supplies | Inventory management, warehouse systems |
| G (General) | The general-purpose supplies used across departments | Office materials, cleaning agents, safety accessories |
PLG supplies are used by small workshops, large industries, construction companies, logistics hubs, and even service-oriented organizations to keep their operations running smoothly.
2. Major Categories of PLG Supplies
PLG supplies are vast and diverse. For better understanding, they can be categorized into several essential groups depending on their purpose and application.
a. Safety Equipment and PPE (Personal Protective Equipment)
Safety is the cornerstone of industrial operations. Personal protective equipment helps reduce workplace accidents and ensures that employees work under secure conditions.
| Type | Examples | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Head Protection | Helmets, hard hats | Prevent head injuries from impact or falling objects |
| Eye and Face Protection | Safety goggles, face shields | Protect against dust, sparks, or chemical splashes |
| Hand Protection | Work gloves, cut-resistant gloves | Prevent abrasions, cuts, and chemical burns |
| Respiratory Protection | Face masks, respirators | Filter harmful airborne particles |
| Foot Protection | Safety shoes, steel-toe boots | Protect from sharp or heavy objects |
| Body Protection | Overalls, reflective vests | Provide full-body protection and visibility |
These items not only comply with safety standards but also boost worker confidence and productivity.
b. Tools and Hardware
Tools are at the heart of all mechanical and construction work. PLG supplies include a wide range of hand tools, power tools, and measuring devices.
| Category | Examples | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Hand Tools | Hammers, pliers, wrenches, screwdrivers | Everyday maintenance and repair tasks |
| Power Tools | Drills, grinders, saws | High-performance tasks requiring power-driven tools |
| Measuring Tools | Levels, measuring tapes, calipers | Ensuring precision and accuracy |
| Cutting Tools | Blades, chisels, saws | Material cutting and shaping |
Well-maintained tools not only enhance performance but also reduce downtime due to malfunctions or inefficiency.
c. Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) Supplies
MRO supplies are essential for keeping equipment and infrastructure in working order. These include lubricants, cleaning materials, adhesives, and fasteners.
| Type | Examples | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Lubrication Supplies | Oils, greases | Reduce friction and wear in machinery |
| Adhesives and Sealants | Glues, tapes, sealants | Repair joints and prevent leaks |
| Cleaning Products | Detergents, disinfectants | Maintain cleanliness and hygiene |
| Fasteners and Fixings | Bolts, nuts, screws | Assembly and equipment maintenance |
Efficient MRO supply management minimizes operational interruptions and extends equipment lifespan.
d. Packaging and Storage Supplies
In logistics and warehousing, proper packaging and storage are critical to protect goods and reduce losses.
| Type | Examples | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Packaging Materials | Boxes, tapes, stretch films | Protect products during handling and shipping |
| Storage Equipment | Racks, pallets, bins | Organize inventory efficiently |
| Labeling and Tags | Barcodes, stickers | Simplify identification and tracking |
| Handling Equipment | Trolleys, pallet jacks | Aid in movement of heavy goods |
Strong packaging solutions also improve brand reputation and ensure safe product delivery.
e. Office and General Supplies
Apart from industrial and safety items, PLG supplies include general office products that support daily administration.
| Category | Examples | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Stationery | Pens, papers, files | For documentation and records |
| Electronics | Printers, calculators | Office operations |
| Cleaning and Hygiene | Sanitizers, mops, tissues | Maintaining workplace hygiene |
| Furniture and Fixtures | Chairs, desks, shelves | Office ergonomics and comfort |
Such supplies ensure smooth internal communication and workflow management.
3. Importance of PLG Supplies in Business Operations
1. Safety and Compliance
PLG supplies play a vital role in ensuring occupational health and safety. Personal protective gear minimizes accidents, while compliant equipment meets regulatory standards such as ISO, OSHA, and ANSI.
2. Operational Continuity
Availability of proper tools, maintenance items, and spare parts ensures uninterrupted operations. Downtime is one of the biggest costs in industries, and efficient PLG management minimizes it.
3. Cost Efficiency
Bulk procurement and supplier optimization help reduce costs. Companies that manage PLG supplies well can negotiate better contracts and reduce wastage.
4. Employee Productivity
Workers equipped with high-quality tools and safety equipment perform tasks more efficiently, confidently, and accurately.
5. Sustainability
Eco-friendly packaging, recyclable materials, and energy-efficient equipment under PLG management contribute to a greener environment.
4. Best Practices in Managing PLG Supplies
a. Accurate Inventory Tracking
An updated inventory system helps monitor stock levels, forecast needs, and avoid both overstocking and shortages.
b. Vendor Management
Establishing long-term relationships with reliable vendors ensures timely deliveries and consistent quality.
c. Quality Control
Routine checks and inspections of tools, safety gear, and materials maintain performance standards and compliance.
d. Digital Procurement Systems
Automation tools and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems simplify ordering, tracking, and replenishment processes.
e. Employee Training
Training staff to properly use, store, and maintain supplies reduces misuse and extends the life of assets.
5. Emerging Trends in PLG Supplies
| Trend | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Inventory Systems | AI and IoT-based stock monitoring | Real-time data and reduced shortages |
| Eco-Friendly Materials | Biodegradable packaging and sustainable PPE | Environmental protection |
| Automation in Procurement | Digital platforms for order management | Speed and accuracy |
| Predictive Maintenance Supplies | Sensors and smart lubricants | Early detection of wear and tear |
| Global Supply Chain Integration | Centralized supply chain networks | Consistent supply and cost control |
These advancements are revolutionizing how companies procure, use, and manage their essential materials.
6. Challenges in the PLG Supply Chain
While PLG supplies are critical, managing them comes with its challenges:
- Supply Chain Disruptions – Natural disasters, pandemics, and geopolitical issues can interrupt the flow of goods.
- Rising Costs – Inflation and raw material shortages can raise procurement costs.
- Counterfeit Products – Unverified suppliers may provide substandard equipment.
- Inventory Mismanagement – Lack of real-time data can lead to losses or delays.
- Regulatory Compliance – Meeting global safety and environmental standards requires constant updates.
Addressing these issues requires strategic planning and technology adoption.
7. Steps to Build an Effective PLG Supply Management System
Step 1: Assessment
Evaluate the types of supplies your organization needs and classify them based on usage and priority.
Step 2: Supplier Selection
Choose suppliers who meet quality, cost, and delivery expectations. Always have backup vendors.
Step 3: Procurement Planning
Use demand forecasting and just-in-time procurement methods to avoid excessive inventory.
Step 4: Storage and Handling
Organize warehouses with proper labeling, shelving, and safety standards.
Step 5: Monitoring and Reporting
Track usage patterns, consumption rates, and supplier performance using digital dashboards.
Step 6: Regular Audits
Conduct quarterly reviews to check for wastage, expired safety items, and maintenance needs.
8. Environmental Responsibility in PLG Supplies
Sustainability is now integral to procurement. Companies are adopting green policies by:
- Using eco-friendly packaging
- Procuring biodegradable cleaning agents
- Recycling worn-out PPE and scrap materials
- Implementing energy-efficient logistics
Sustainable PLG supplies reduce environmental impact and enhance corporate reputation.
9. Case Example (Illustrative)
A mid-sized manufacturing company introduced a digital PLG management system integrating procurement, logistics, and inventory control. Within one year, the firm reported:
| Parameter | Before | After |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory Errors | 23% | 3% |
| Procurement Time | 10 days | 2 days |
| Operational Downtime | 15 hours/month | 4 hours/month |
| Annual Cost Savings | – | 18% |
This example shows how organized PLG supply management can transform business performance.
10. Future of PLG Supplies
The future of PLG supplies is defined by digitization, sustainability, and customization. AI-driven procurement tools will predict demand, automate supplier evaluation, and track deliveries in real time. In addition, smart PPE embedded with sensors will monitor worker safety more effectively. Companies investing in these technologies will stay ahead in productivity, compliance, and cost control.
Conclusion
PLG supplies are far more than just items of convenience—they are the foundation of safe, productive, and sustainable industrial operations. From protective gear and tools to packaging materials and maintenance supplies, their effective management can significantly impact business performance.
Organizations that adopt a systematic approach—focusing on procurement accuracy, logistics efficiency, and environmental responsibility—can achieve long-term operational excellence. Investing in quality PLG supplies is, therefore, an investment in the future of safety, productivity, and profitability.
FAQs
1. What are PLG supplies used for?
PLG supplies are used for daily industrial, construction, and maintenance activities, ensuring safety, efficiency, and operational continuity.
2. What are examples of PLG supplies?
Examples include safety helmets, gloves, hand tools, packaging materials, lubricants, and cleaning agents.
3. Why are PLG supplies important?
They ensure worker safety, reduce downtime, enhance productivity, and help businesses comply with industrial regulations.
4. How can companies manage PLG supplies efficiently?
By using inventory management systems, maintaining vendor relationships, conducting audits, and training staff for proper use.
5. Are PLG supplies environmentally friendly?
Many modern suppliers now offer eco-friendly options such as recyclable packaging, biodegradable cleaning products, and reusable safety gear.